Overview of the B61-12 Nuclear Bomb
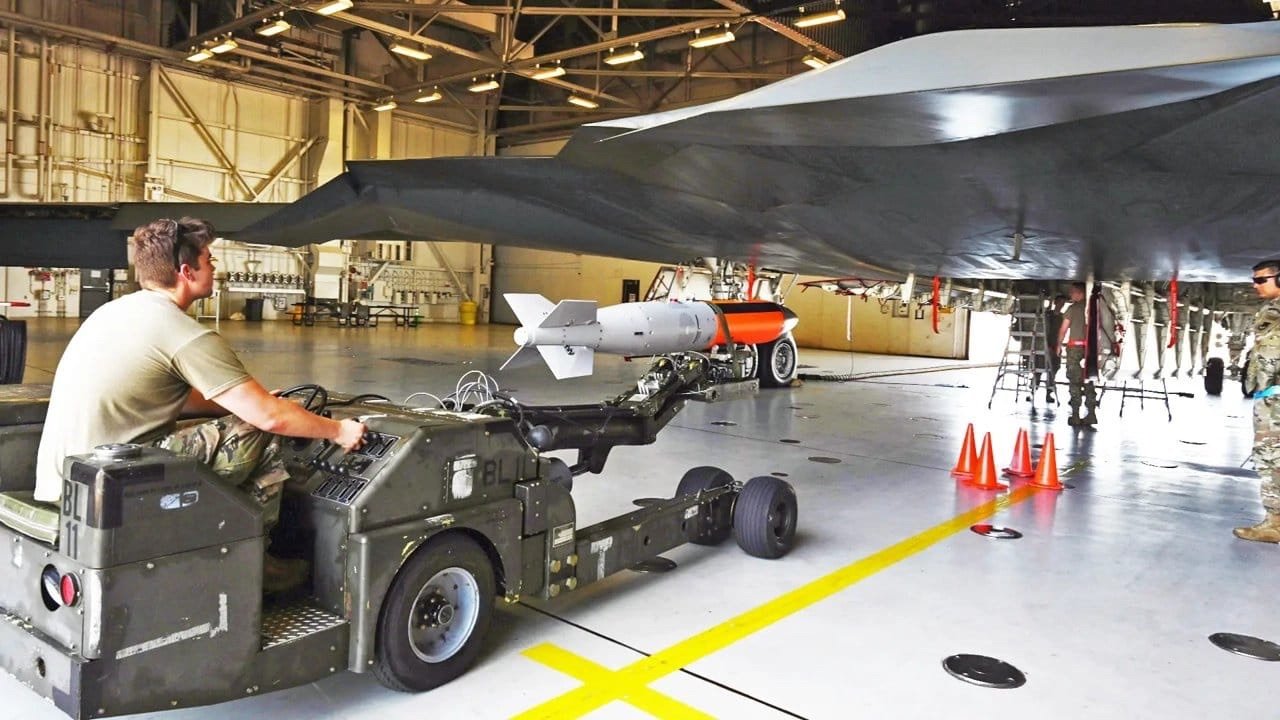
The B61-12 is the latest iteration in the B61 family of nuclear bombs, originally developed during the Cold War. It is a variable yield, gravity nuclear bomb designed for strategic and tactical use.

Modernization of Nuclear Capabilities: The United States is actively modernizing its nuclear capabilities, specifically focusing on the B61-12 nuclear bombs. These efforts include updating the infrastructure that supports nuclear sharing missions in Europe, with plans to deploy these new bombs to European air bases for delivery by both U.S. and allied aircraft.

Accelerated Deployment: Originally scheduled for deployment in Spring 2023, there were reports of an accelerated schedule for the B61-12 bombs, proposing a new timeline of December 2022. This accelerated deployment was intended for U.S. European bases, as revealed by diplomatic sources. However, a senior Pentagon official reportedly dismissed these accelerated deployment reports, maintaining that there was no change in the timeline.
Life Extension Program: The B61-12 bomb is part of a life extension program, which is a significant step in modernizing the United States’ tactical nuclear munitions. This program aims to update older munitions, bringing them into the modern era with enhanced capabilities.
Future Upgrades and Testing: In addition to the B61-12, there are plans for further upgrades. The Biden administration proposed another upgrade named B61-13, which is expected to have greater explosive force than the B61-12. Notably, an F-35 released an unarmed B61-12 nuclear gravity bomb in a test in 2019, demonstrating the ongoing development and testing of these nuclear capabilities.

Design and Development
- Manufacturer: The bomb was developed by the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), a part of the U.S. Department of Energy, in collaboration with the U.S. Air Force.
- Development Program: Part of the Life Extension Program (LEP), aiming to consolidate and replace older versions of the B61.
- First Production Unit: Completed in 2020.
Technical Specifications
- Length: Approximately 3.58 meters.
- Diameter: Around 33 centimeters.
- Weight: About 320 kilograms.
- Yield: Variable, can be adjusted before deployment; options range from 0.3 to 50 kilotons.
- Guidance System: Incorporates a Boeing-built tail kit for increased accuracy, using Inertial Navigation System (INS) and satellite guidance.
- Delivery Platforms: Compatible with a variety of aircraft, including B-2 bombers, F-15, F-16, and the new F-35 stealth fighters.

B61-12 Nuclear Bomb - Historical Overview- Origins: The B61 nuclear bomb series, originating in the 1960s, is a key component of the United States’ nuclear arsenal, designed during the Cold War.
- Development: The B61-12 is the most recent upgrade, part of a life extension program to modernize and consolidate various B61 variants.
Specifications
- Physical Characteristics: Approximately 12 feet in length, weighing around 825 pounds.
- Yield Flexibility: The bomb has a variable yield, adjustable from 0.3 to 50 kilotons.
- Guidance System: Equipped with an inertial navigation system (INS) and a precision-guided tail kit.
- Compatibility: Designed for delivery by a variety of aircraft, including B-2 and upcoming B-21 stealth bombers, F-35, F-15, and F-16 fighters.
Strategic Importance
- Modernization and Safety: Represents a significant modernization of the U.S. nuclear arsenal, with enhanced safety and security features.
- Deterrence and Flexibility: Its adjustable yield and improved accuracy bolster nuclear deterrence capabilities and operational flexibility.
- Global Security: Plays a pivotal role in U.S. strategic nuclear posture and has implications for NATO’s defense strategy.
Integration and Deployment
- Current Status: Integrated into the U.S. nuclear stockpile, with ongoing certification for various aircraft.
- Testing: Underwent extensive testing, including with the B-2 Spirit bomber, to ensure reliability and effectiveness.
Future Developments
- B61-13 Development: Plans for a new variant, B61-13, with a higher yield and similar safety features, are underway.
Strategic Importance
The B61-12 is viewed as a critical component in the U.S.’s extended deterrence strategy, especially in the context of NATO’s defense posture in Europe.
Enhanced Capabilities
- Increased Accuracy: The new guidance system significantly improves accuracy, reducing the need for larger yields for the same strategic effect.
- Flexibility: The adjustable yield allows for tailored strategic and tactical use, making it versatile for various scenarios.
- Survivability: Enhanced compatibility with modern stealth aircraft enhances survivability and delivery assurance.
Geopolitical Implications
- NATO Assurance: Reinforces the U.S. commitment to NATO’s defense, particularly in Eastern Europe.
- Global Deterrence: Serves as a deterrent to potential adversaries like Russia and China.
- Arms Control Challenges: May impact future arms control negotiations, especially with regards to tactical nuclear weapons.
Controversies and Concerns
- Cost: The LEP for B61-12 is expensive, raising questions about budgetary priorities.
- Nuclear Proliferation: Critics argue it might stimulate a new arms race and undermine global non-proliferation efforts.
- Strategic Stability: Some experts fear that its increased accuracy could lower the threshold for nuclear use.
The deployment of the B61-12 nuclear bombs represents a significant milestone in modernizing the U.S. nuclear arsenal. While enhancing deterrence and assurance capabilities, it also poses challenges for global arms control and non-proliferation efforts. The ongoing debate reflects the complex dynamics of contemporary nuclear strategy and international security.